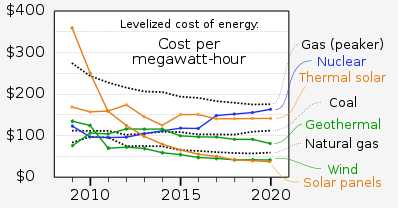
A battery likewise stores its energy in a substance structure. It can utilize its energy to let electrons out of atoms. Electrons can convey their energy along metal wires and convey their energy somewhere else; consider wires pipes for electrons. The central benefit of electric energy is that it very well may be handily shipped along wires and changed over completely to movement with an electric engine. A vehicle battery contains multiple times less energy than an equivalent load of fuel! Indeed, even a costly PC battery is multiple times more awful than gas. Those are the physical science motivations behind why most cars use gas rather than batteries as their wellspring of energy. Batteries are utilized to turn over the motor since they are dependable and quick- Power to Choose .
Battery-powered vehicles
A run-of-the-mill auto battery is likewise called a lead-corrosive battery since it utilizes the substance response between lead and sulfuric corrosive to create power. The table shows that such batteries convey multiple times less energy than gas. Be that as it may, the electric energy from a battery is extremely helpful. It very well may be changed over completely to wheel energy with 85% proficiency; put another way, just 15% is lost in running the electric engine. A fuel motor is a lot more terrible: just 20% of the energy of gas comes to the wheels; the excess 80% is lost as heat. At the point when you put in those factors, the upside of gas is diminished from 340 down to an element of 80. In this way, for cars, batteries are just multiple times more regrettable than gas. That number is adequately little to make battery-driven cars possible. A run-of-the-mill vehicle gas tank holds around 100 pounds of gas. To have batteries that convey the energy in 100 pounds of fuel would take multiple times that weight, that is to say, 800 pounds of batteries. In any case, assuming that you will split the scope of the vehicle, from 300 miles to 150, then the weight is down to 400 pounds. If you just need 75 miles to drive, the weight is just 200 pounds.
How could you exchange a gas vehicle for one that could go just 75 miles?
The typical inspiration is to set aside cash. Power purchased from the power organization, used to charge the battery, costs just a dime for each kWh. At the point when you make an interpretation of that into energy conveyed to the wheels, that works out to around 40 pennies for each kWh. So power is multiple times less expensive! It isn’t exactly mind-blowing. At the point when the vast majority resolve those numbers, they overlook the way that standard lead-corrosive vehicle batteries must be supplanted later, normally, 700 charges. At the point when you incorporate the battery cost, the expense per kWh is around 20 pennies for each kWh. It beats the expense of fuel by a component of two. But since batteries take up such a lot of room, not an alluring choice for individuals to esteem trunk space. Batteries enjoy extra benefits in certain conditions. In The Second Great War, when submarines needed to lower and couldn’t get oxygen, their energy source was an immense number of batteries put away underneath the decks. At the point when, by all accounts, or “swimming profundity,” the submarines ran on diesel fuel, a type of gas. The diesel fuel likewise ran generators that re-energized the batteries. So during WWII, most submarines invested a large portion of their energy on the surface, re-energizing their batteries. Watch an old The Second Great War film, and they don’t show that; you get the misimpression that the subs were dependably beneath the water. Current nuclear submarines don’t need oxygen, and they can stay lower for quite a long time. That incredibly expands their protection from the location.

